Introduction
The world has been steadily transitioning towards digitization in all aspects, and the business ecosystem is no exception.
As a result, eCommerce, or electronic commerce, has significantly transformed the way businesses are conducted around the globe.
According to Statista, in 2021, retail e-commerce sales amounted to approximately 5.2 trillion U.S. dollars worldwide. This figure is forecast to grow by 56 percent over the next years, reaching about 8.1 trillion dollars by 2026.
This demonstrates the massive growth and potential eCommerce holds in today's digital age.
If you're new to eCommerce or simply want a deeper understanding of this dominant aspect of modern trade, this comprehensive guide will provide useful insights.
What is eCommerce?
eCommerce, short for electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods or services using the internet.
It also encompasses the transfer of money and data to execute these transactions.
eCommerce is often used to refer to the sale of physical products online, but it can also depict any kind of commercial transaction that is facilitated through the internet.
Beyond this basic definition, eCommerce includes various online activities, such as internet banking, online auctions, and ticketing.
One of the most distinguishing features of eCommerce is its capacity to break geographical barriers, allowing businesses to reach global markets around the clock.
Different Types of eCommerce Models
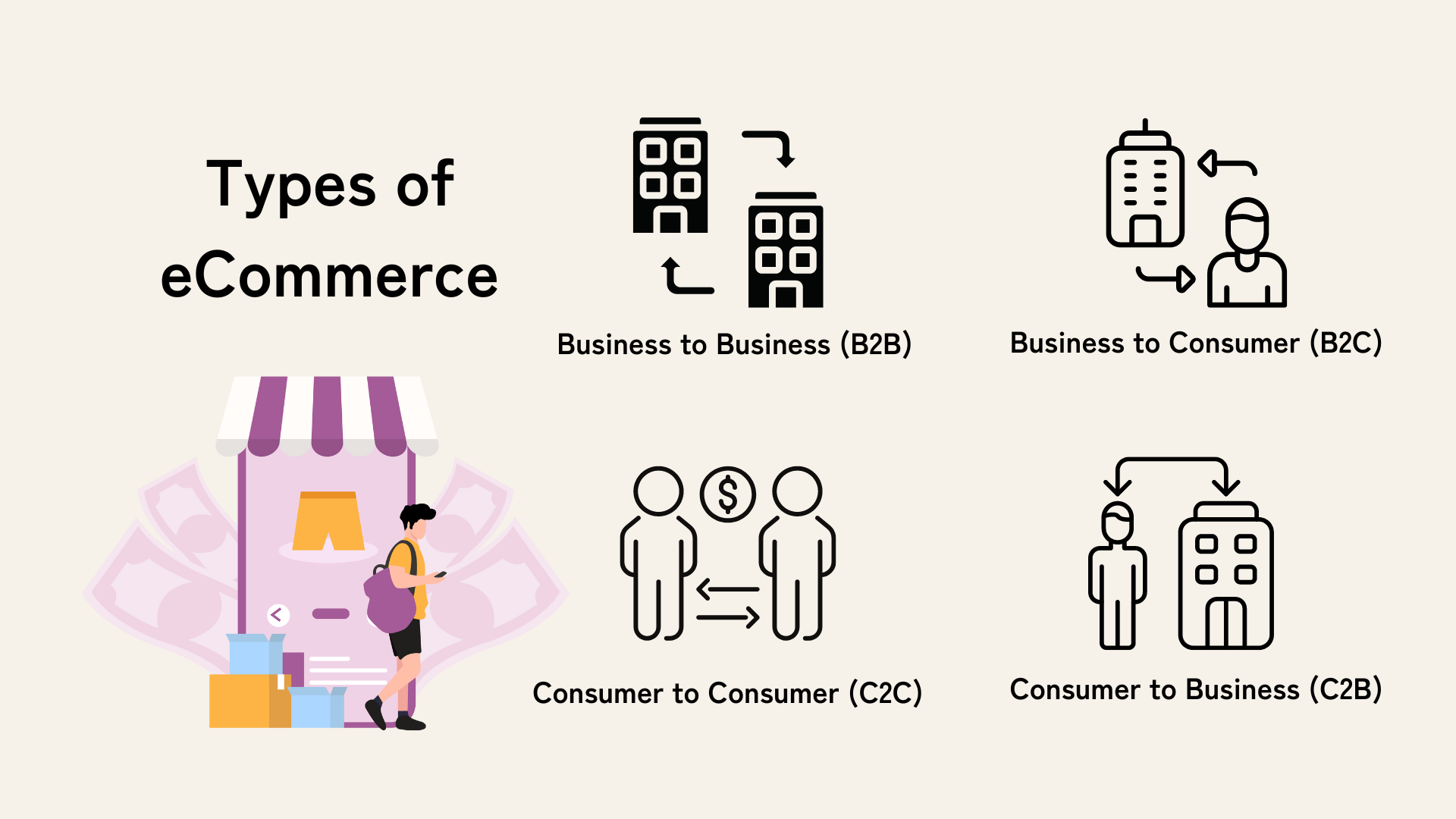
- Business to Business (B2B): As the name suggests, B2B eCommerce refers to transactions conducted between two businesses. This often involves wholesalers selling products in large quantities to retailers.
- Business to Consumer (B2C): This model involves businesses selling directly to consumers. This is the most commonly understood form of eCommerce, depicted by companies like Amazon and eBay.
- Consumer to Consumer (C2C): In this model, consumers trade with other consumers. Platforms like eBay and Craigslist facilitate such transactions.
- Consumer to Business (C2B): This model flips the traditional B2C model, allowing consumers to sell their goods or services to businesses. Examples include freelance services, product reviews, or crowdsourcing platforms like Kickstarter.
How Does eCommerce Work?
The success of any eCommerce business relies on various interconnected processes and systems. Here's an overview to illustrate the typical workflow:
#1 Attracting Customers
Businesses must effectively market their products/services and drive traffic to their website or online marketplace.
Digital marketing strategies like search engine optimization (SEO), social media marketing, and email campaigns play a crucial role.
#2 Presenting Products/Services
Once customers visit your eCommerce website or online marketplace, you need to display your products or services attractively. Your online catalog should include high-quality images, detailed descriptions, and customer reviews.
Consider how Apple displays its products on its website, along with technical specifications and clear, high-resolution images, allowing product differentiation.
#3 Order Placement
When customers add products/services to their shopping cart and proceed to checkout, your website should offer an intuitive process.
Clear pricing, transparent shipping, guest checkout, and multiple payment methods are essential.
The online apparel retailer ASOS offers an easy-to-use checkout process. It allows customers to store multiple addresses, use store credits, and select from various shipping and payment options.
#4 Secure Payment Processing
When a customer completes the checkout process, a secure payment gateway is responsible for encrypting and processing payment information safely.
An example of a popular payment gateway is PayPal. Not only does it securely handle transactions, but it also offers buyer protection, instilling customer confidence and trust.
#5 Order Fulfillment
After an order has been placed and paid for, your eCommerce platform should notify the respective warehouse or fulfillment center to prepare the shipment.
Integration with inventory management systems is crucial to track stock levels and prevent overselling.
For instance, Shopify, a popular eCommerce platform, offers integrated fulfillment solutions, enabling merchants to track product availability and manage orders efficiently.
#6 Shipping & Delivery
After an order is packed and dispatched, it is transported to the customer using shipping carriers (e.g., FedEx, UPS, or DHL).
Providing customers with estimated delivery times, tracking numbers, and transparent charges can improve the overall shopping experience.
Etsy, an online marketplace for handmade goods, allows sellers to choose from various shipping carriers and offers customers the ability to track their orders.
#7 Customer Support & Retention
Providing excellent customer support and handling returns, refunds, or exchanges professionally is essential for eCommerce success.
Effective post-purchase communication, personalized offers, and loyalty programs will help businesses retain satisfied customers.
Take Zappos, an online shoe retailer, known for its outstanding customer service. From hassle-free returns to 24/7 live chat support, Zappos puts customers first.
The Pros and Cons of eCommerce
The increasing rise of eCommerce over the past decade is undeniable, but like all business models, it has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Understanding both sides is essential for businesses looking to make a mark in the online market.
Advantages of eCommerce
- Wider Customer Reach: eCommerce eliminates geographical boundaries, allowing businesses to reach national and even international markets effortlessly. This vastly expanded customer base leads to more potential sales, thereby increasing revenue.
- Operational 24/7: eCommerce businesses are always open, allowing customers to make purchases at any time, from anywhere. This around-the-clock service leads to greater customer satisfaction and potential for higher sales.
- Lower Operational Costs: Without the need for physical stores, the costs of maintaining an eCommerce business, such as rent, utilities, and additional staff, are significantly lower. This factor allows businesses to improve their profit margins.
- Easy Price and Product Comparison: Customers can easily compare prices, features, and reviews of multiple products online, increasing the chances of informed purchasing decisions. This transparency also encourages businesses to offer competitive pricing and quality products.
- Personalized Experiences: eCommerce platforms allow customization of user experiences through targeted marketing, personalized recommendations, and tailor-made deals and offers.
Disadvantages of eCommerce
- Customer Trust: In the absence of physical interaction with products or sales staff, building trust is a significant challenge. Issues relating to online security and privacy can also affect customers' willingness to purchase.
- Dependence on Technology: The success of eCommerce is entirely reliant on internet connectivity and power supply. Technical issues, downtime, or a slow website can significantly impact sales and customer satisfaction.
- Competition: The ease of setting up an eCommerce business has led to a saturated market, with numerous competitors for virtually every product category. Setting your brand apart in such a crowded marketplace can be challenging.
- Lack of Personal Interaction: Shopping is often seen as an experience, where you can touch the product, get immediate help from sales staff, or even enjoy it as a social activity. eCommerce lacks this personal interaction, which can affect certain product categories.
- Return and Refund Complications: Handling returns and refunds can be a complex process in eCommerce. The customer dissatisfaction from receiving a wrong, damaged, or unsatisfactory product can be compounded by the inconvenience of returning the item.
Key Components of a Successful eCommerce Business

Now that we understand the significance of eCommerce let's delve into its key components:
#1 Website Design
A well-designed, user-friendly website is crucial for any eCommerce business. The design should align with your brand image, be easy to navigate, and offer a seamless checkout process.
A responsive design that adapts to different devices is also crucial to cater to the growing mobile commerce (mCommerce) trends.
#2 Product Catalog
A thorough and well-organized product catalog is essential to provide customers with detailed information about your products.
High-quality images, specific product descriptions, and customer reviews can enhance product visibility and influence purchase decisions.
#3 Shopping Cart and Checkout Process
A simplified shopping cart and checkout process can significantly reduce cart abandonment.
Offering a guest checkout option, multiple payment methods, and transparent shipping information will enhance the customer shopping experience.
#4 Secure Payment Gateway
Security is a top concern in eCommerce. Ensuring a secure payment gateway that safely processes customer information is vital to build trust and retain customers.
#5 Customer Service
Providing excellent customer service in eCommerce involves responsive communication channels, easy returns and exchanges, and post-purchase support.
According to Jeff Bezos, founder of Amazon, "The best customer service is if the customer doesn't need to call you, doesn't need to talk to you. It just works." eCommerce is essentially an endeavor to make things 'just work', making shopping convenient, fast, and user-friendly.
Conclusion
eCommerce has become an undeniable part of our everyday lives and a critical revenue channel for businesses across the globe.
From providing a consolidated understanding of eCommerce, its workflow, advantages, disadvantages, history, and market potential, this guide aimed to provide you all the necessary pointers for grasping the realm of eCommerce.
While the digital sphere is filled with opportunities, the competition is stiff. To stand out, an eCommerce business needs a thoughtful strategy that considers customer experience, reliable and quality products or services, and robust site functionality.
In the rapidly evolving eCommerce landscape, staying flexible to incorporate emerging technologies, trends, and customer preferences can lead to continued success.