Introduction
In today's fast-paced business landscape, mastering the art of logistics management has become more crucial than ever.
Logistics management stands at the heart of this complex process, ensuring the seamless flow of goods through the supply chain.
It's a dance of planning, execution, and monitoring, where precision meets agility. But how do you navigate this intricate world without getting lost in its complexity?
This comprehensive guide dives into the essentials of logistics management, its functions, importance, types, and more, all written in a comprehensive language perfect for beginner business enthusiasts.
What is Logistics Management?
The Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals (CSCMP) defines logistics management as "the part of supply chain management that plans, implements, and controls the efficient, effective forward and reverse flow and storage of goods, services, and related information between the point of origin and the point of consumption in order to meet customers' requirements.”
In more straightforward language, logistics management is about ensuring that the right products are delivered to the right location, on time, in the optimal condition and quantity, and at the right price.
It encompasses a wide array of processes including procurement, transportation, storage, and distribution, all aimed at meeting customer demands while minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency.

The Logistics Management Process Explained
Demand Planning and Forecasting:
Anticipating customer demand is the foundation of logistics management.
Businesses must predict the quantity and type of products consumers will purchase.
This step involves data analysis, market trends, and historical sales figures to ensure that the inventory levels are aligned with consumer demand.
Sourcing and Procurement:
Once demand is forecasted, the next step is securing the raw materials or products needed to meet that demand.
Sourcing involves selecting suppliers that offer the best value in terms of quality, cost, and delivery times.
Effective procurement is about negotiating contracts and maintaining a smooth flow of goods into the business.
Inventory Management:
Holding either too much or too little inventory can have significant financial implications.
Efficient inventory management ensures that there is enough stock to meet demand without excessive overstock which ties up resources.
It includes the organization, storage, and replenishment of goods in a way that balances cost against service level to customers.
Warehouse Management:
This process entails the physical aspect of storing goods until they are sold or shipped out.
It covers receiving, storing, and tracking inventory to ensure quick, accurate order fulfillment.
Modern warehouse management often relies on sophisticated software to optimize storage and minimize handling costs.
Transportation:
Moving products from the warehouse to the customer - or between any points in the supply chain - involves careful planning of both the modes of transport (air, sea, rail, truck) and the logistics routes.
Cost, speed, and reliability are key considerations in selecting transportation options to ensure timely delivery and customer satisfaction.
Order Fulfillment:
Fulfilling customer orders is the culmination of the logistics process. It includes everything from processing customer orders, picking and packing the correct items, to shipping them out.
Efficient order fulfillment is crucial for maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Returns Management (Reverse Logistics):
Handling returns smoothly is an integral part of logistics management, especially in the eCommerce era.
This step deals with the process of accepting returned items, assessing them, and either restocking, disposing, or redirecting the goods as necessary.
Continuous Improvement and Optimization:
The logistics management process doesn’t end with shipping the product.
Continuous analysis of data and feedback is essential for identifying areas for improvement.
By constantly seeking ways to reduce costs, shorten delivery times, and improve service quality, businesses can retain a competitive edge.
Functions of Logistic Management

Logistics management plays a pivotal role in ensuring the seamless movement of goods from suppliers to end-users, a process fundamental to the success of businesses globally.
Understanding the key functions of logistics management can empower businesses to optimize their operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and improve their bottom line.
1. Order Fulfillment
Order fulfillment is at the heart of logistics management and involves processing customer orders accurately and delivering them in a timely fashion.
It's a multistep process that includes order receipt, processing, picking, packing, and shipping. Efficient order fulfillment is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty.
According to a study by the National Retail Federation, fast and reliable shipping is one of the primary factors influencing consumers' purchasing decisions.
2. Transportation Management
Transportation is the lifeblood of logistics, enabling the physical movement of goods from suppliers to customers.
This function includes selecting the most effective modes of transport (road, rail, air, or sea), route planning, and optimizing loads to reduce costs and transit times.
Strategic transportation planning ensures that products not only reach their destinations on time but also in a cost-effective manner.
3. Inventory Control
Inventory control is the regulation of inventory levels to meet demand without incurring excess costs or stockouts.
It involves activities such as stock monitoring, forecasting demand, and setting reorder points.
Effective inventory control is vital for minimizing holding costs while ensuring product availability.
4. Warehousing and Storage
This function involves the safekeeping of goods until they are needed by the next link in the supply chain.
Warehousing decisions, such as location selection, layout, and automation, directly impact a company's efficiency in processing orders and distributing products.
Modern logistics demands flexible warehousing solutions that can accommodate fluctuating stock levels, enhancing a business's ability to respond to market demands swiftly.
As the Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals (CSCMP) outlines, modern warehousing solutions include advanced technologies like warehouse management systems (WMS) and robotics to enhance operational effectiveness.
5. Demand Planning
Demand planning anticipates customer demand to align inventory levels and production schedules accordingly.
This strategic function involves analyzing market trends, historical sales data, and customer feedback to forecast future demand.
Demand planning is a cornerstone of effective supply chain management, enabling companies to adjust their strategies proactively.
6. Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics manages the return process for goods, encompassing activities from the point of return initiation to the final disposition of the returned goods.
This includes returns due to defects, customer dissatisfaction, or end-of-life recycling.
A robust reverse logistics function is increasingly important for sustainability and customer service.
7. Customer Service
While often overlooked, customer service is a critical function of logistics management.
It encompasses providing timely and accurate information to customers regarding product availability, order status, and delivery tracking.
Excellent customer service ensures a positive buying experience, fostering loyalty and repeat business.
A report by Salesforce highlights that 80% of customers consider their experience with a company to be as important as its products.
Importance of Logistic Management

Logistics management has emerged as a key determinant of business success.
It goes beyond the mere transportation of goods, encompassing a wide array of activities aimed at efficiently moving products from suppliers to customers.
Here are the importance of logistics management and how it can be a game-changer for businesses, especially for those just stepping into the complex world of supply chain management.
1. Enhances Customer Satisfaction
At its core, logistics management is about delivering the right product, in the right quantity and condition, at the right place and time.
This precision is crucial for meeting or exceeding customer expectations, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
An effective logistics strategy leads to higher customer satisfaction rates, which in turn can result in increased repeat business and positive word-of-mouth.
2. Reduces Operational Costs
Efficient logistics management enables businesses to identify and leverage cost-saving opportunities throughout the supply chain.
By optimizing routes, consolidating shipments, and managing inventory smartly, companies can significantly reduce transportation, warehousing, and holding costs.
Companies can save up to 35% in logistics costs through effective logistics management, freeing up resources that can be invested in other business areas.
3. Improves Efficiency and Productivity
A streamlined logistics operation minimizes waste—be it time, resources, or effort—and maximizes output.
Implementing technologies like Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Transportation Management Systems (TMS) can automate routine tasks, reduce errors, and improve operational efficiency.
4. Supports Business Growth
Growth-oriented businesses often face the challenge of scaling their operations while maintaining service quality.
Effective logistics management provides a scalable framework that accommodates growth without compromising on efficiency or customer satisfaction.
It allows businesses to explore new markets, handle increased order volumes, and manage a growing network of suppliers and distributors.
5. Increases Supply Chain Visibility
Visibility throughout the supply chain is vital for making informed decisions.
Logistics management utilizes advanced tracking and monitoring systems to provide real-time data on shipments, inventory levels, and supply chain performance.
This visibility aids in forecasting, risk management, and strategic planning.
6. Enhances Sustainability
The global push towards sustainability has made eco-friendly practices a necessity.
Logistics management plays a crucial role in designing green supply chains, optimizing routes for reduced fuel consumption, and employing sustainable packaging solutions.
Such efforts not only contribute to environmental preservation but also resonate well with increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
Types of Logistic Management
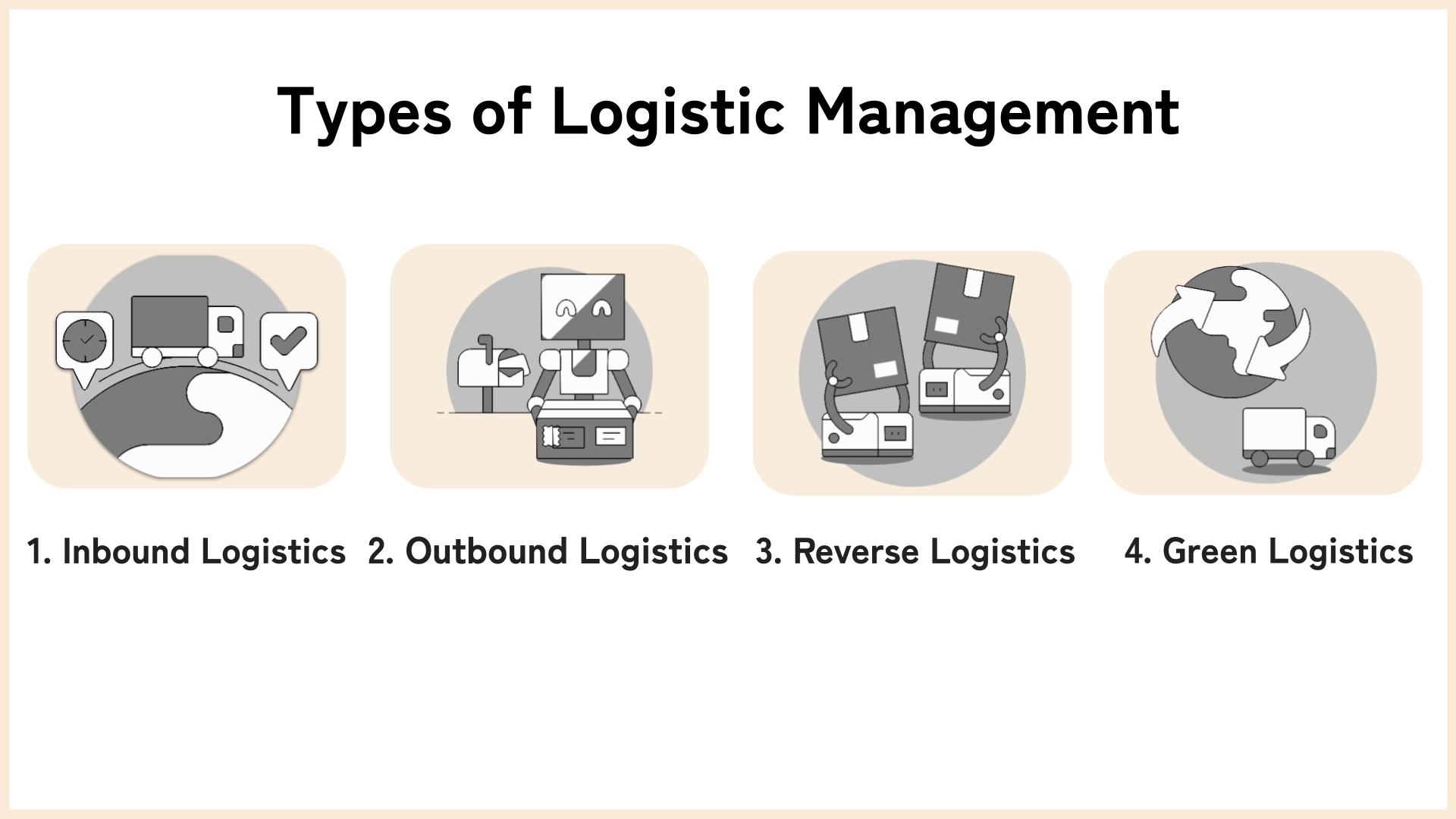
Grasping the fundamental types of logistics management is vital to ensure optimal supply chain operations.
Let’s break down these these types of logistics management to help you crafting tailored strategies!
1. Inbound Logistics
Inbound logistics refers to the procurement and transportation of raw materials and goods from suppliers to manufacturing or processing plants.
This logistics type is fundamentally concerned with the supply side of the supply chain, ensuring that materials arrive safely, timely and cost-effectively.
By managing inbound logistics efficiently, businesses can reduce costs, improve production times, and enhance product quality.
Key aspects of inbound logistics include supplier relationship management, cost negotiations, inventory control, and transportation management.
The ultimate goal is to streamline operations in a way that they align seamlessly with production schedules.
2. Outbound Logistics
Outbound logistics is the process that involves the movement of finished goods from the company to the end user. It encompasses all the steps involved in warehousing, packaging, and transportation to distributors, wholesalers, or directly to consumers.
Outbound logistics focuses on the demand side, ensuring that the distribution of finished products is handled efficiently, cost-effectively, and within delivery timelines.
A primary challenge in outbound logistics is managing the distribution network, which may include various transportation modes and delivery points.
Effective outbound logistics can enhance customer satisfaction and reduce operational costs through optimized shipping routes and methods.
3. Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics entails the process of moving goods from their typical final destination for the purpose of capturing value, or proper disposal.
It is most commonly associated with the returns of goods from consumers, but it also includes recycling, refurbishment, and disposal.
Implementing efficient reverse logistics is crucial as it affects customer satisfaction, environmental impact, and cost management.
Reverse logistics can be complex to manage as it involves additional tracking, inventory management, and quality control.
However, businesses that excel in reverse logistics stand to benefit from reduced waste, increased reusability of materials, and enhanced customer service.
4. Green Logistics
Green logistics aims to minimize the environmental impact of logistics activities. It involves implementing practices that reduce energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste.
This logistics type is gaining traction as consumers and regulatory bodies increasingly demand environmentally responsible business practices.
Green logistics can include the use of alternative fuel vehicles, energy-efficient warehousing, optimized routing to reduce mileage, and sustainable packaging materials.
Although transitioning towards green logistics can involve upfront costs, it often leads to long-term savings and a stronger brand image.
Conclusion
Logistics management is an indispensable part of successful business operations, directly influencing cost-efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall productivity.
As we've explored the vast landscape of logistics management, the journey from understanding its fundamentals to implementing efficient practices might seem daunting.
Yet, the path to transforming your logistics operations from a maze of challenges into a streamlined powerhouse of efficiency is clear.
By understanding its core functions, importance, types, and processes, and by implementing strategic improvements, businesses of all sizes can achieve a competitive edge in today’s dynamic market.
Why wrestle with the complexities when Sanka offers an all-in-one solution that simplifies and automates your logistics management?
From procurement and inventory management to orders and shipping, Sanka equips you with the tools to manage them all, seamlessly integrating with your current systems.
Take the first step towards revolutionizing your logistics management.
Experience the power of Sanka and streamline your operations like never before. Start your journey with Sanka today – because when logistics becomes this easy, there’s no limit to where your business can go.