Introduction
Welcome to the energizing world of supply chain management! Whether you're a budding entrepreneur, a business student, or just curious, understanding the nuts and bolts of the supply chain is crucial in today's interconnected economy.
Supply Chain Management is the backbone of commerce, connecting various entities and processes involved in the production and distribution of goods and services.
From sourcing raw materials to delivering products to consumers, the supply chain encompasses a complex network that needs efficient management to ensure smooth operations and customer satisfaction.
Whether you aim to manage a supply chain department, run your own business, or simply gain a better understanding of this vital business function, this guide is your starting point.
Let's embark on this educational journey together, exploring the fascinating dynamics that keep the wheels of commerce in motion.
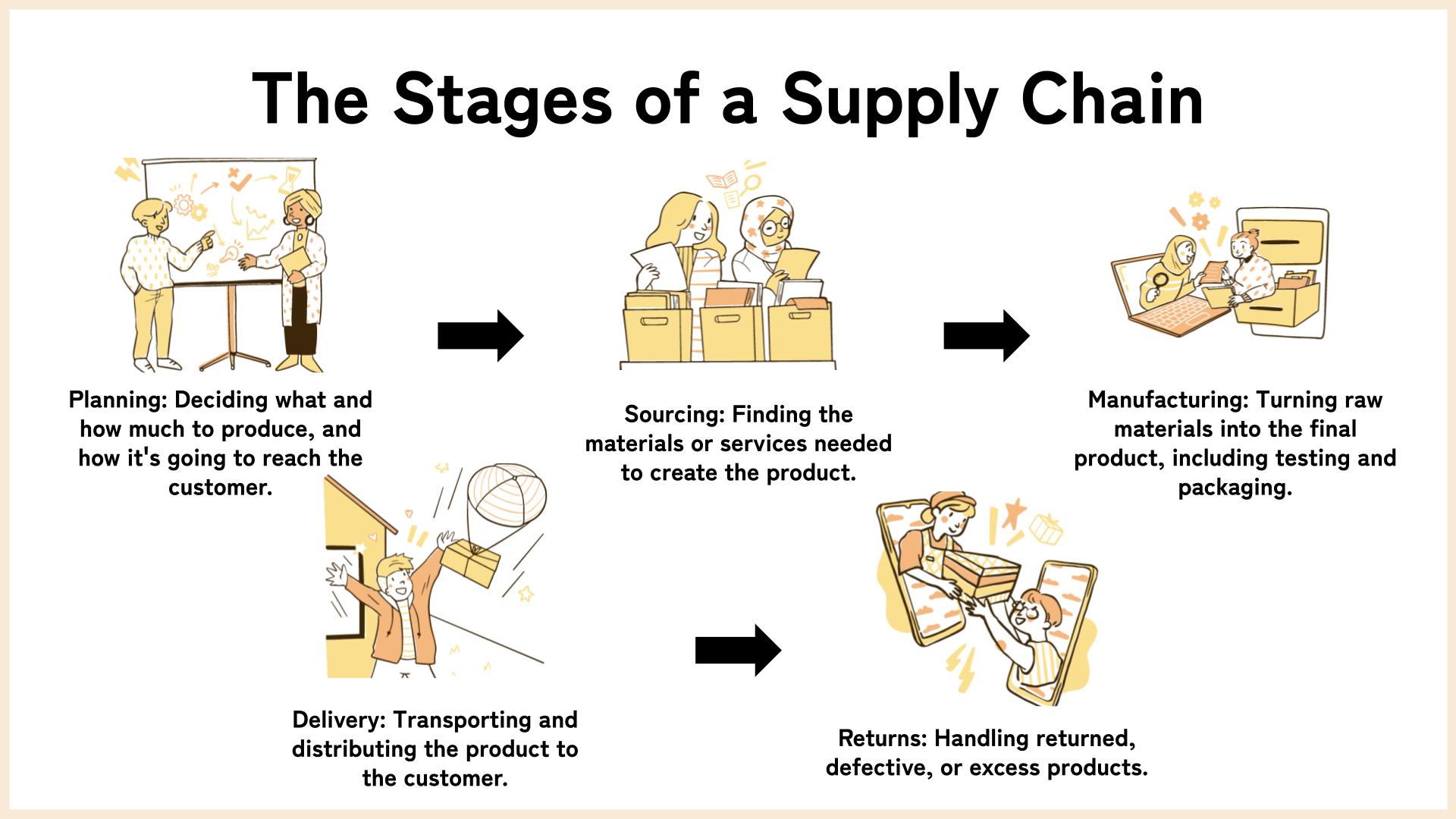
What is a Supply Chain?
A supply chain can be viewed as the backbone of any product-based business.
It is a complex network that encompasses every step involved in bringing a product from its conception to the consumer.
This includes sourcing raw materials, production, distribution, and ultimately, the sale of the final product.
But why is it called a 'chain'? Because traditionally, this process was viewed as a series of interconnected links, each dependent on the one before it.
Imagine you're planning a massive dinner party. You need ingredients, utensils, and maybe even some decorations.
Now, think about how all those items got to you. They were probably grown, manufactured, or crafted by different people, in different places, then brought together through a series of steps.
That is a supply chain in its simplest form! It’s the journey a product takes from its raw material stage to being in the hands of the final customer.
Supply Chain Process Examples
Seeing a concept in action can significantly enhance our understanding. Let’s embark on a journey through the supply chain of a seemingly simple, yet intricately complex product for example your cup of coffee.
This practical illustration will help beginners grasp how each step in the supply chain plays a vital role in delivering that perfect latte to your table.
1. Sourcing the Beans
Our journey begins in the lush green fields of coffee farms, possibly located in countries renowned for their coffee production.
The process of sourcing involves selecting the highest-quality beans, a critical decision that sets the foundation for the end product's taste and quality.
The choice of farm, the method of cultivation, and even the harvesting technique can significantly impact sustainability practices and the social fairness of the trade, setting the ethical tone for the entire supply chain.
2. Processing the Beans
Once harvested, coffee beans go through a series of processes, including drying, hulling, and sometimes, even fermenting.
This can happen on the farm itself or at a nearby processing facility.
The quality of processing impacts the flavor profile of the beans and thus, the quality of your coffee.
3. Global Delivery
After processing, the beans are packed and shipped worldwide. This delivery phase involves intricate logistics, including storage, transportation, and customs clearance, ensuring the beans arrive at their next destination in good condition.
This phase of the supply chain highlights the importance of managing relationships with logistics partners and the need for meticulous planning to manage delivery times, costs, and the environmental impact of transportation.
4. Brewing the Perfect Cup
Once the beans arrive at your coffee shop, you undergo roasting, which is where you develop their rich colors and flavors.
After roasting, the beans are ground to a specific coarseness or fineness, depending on the brewing method.
The final step, brewing, is where art meets science, transforming ground coffee and water into the latte you know and love.
5. Handling Returns: A Fault in the Beans
In any supply chain, the potential for returns or complaints regarding product quality is present.
Should there be an issue with the coffee beans—perhaps they’re stale or contaminated—it’s essential they can be returned or replaced efficiently.
This phase emphasizes the need for strong communication lines within the supply chain and a commitment to customer satisfaction.
Managing returns involves more than just replacing faulty goods; it also offers an opportunity to analyze what went wrong and improve the sourcing, processing, or delivery stages to prevent future issues.
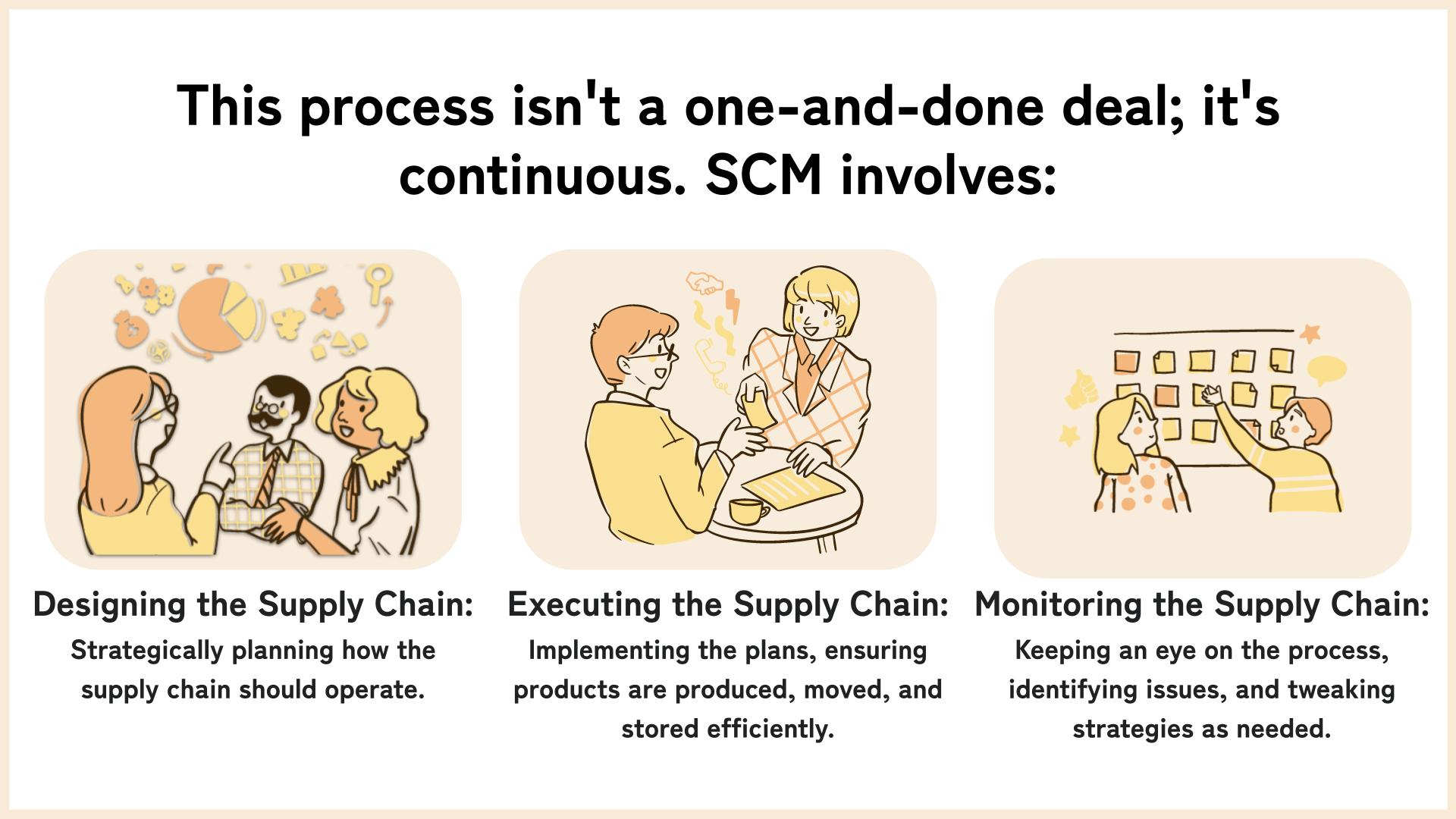
What is Supply Chain Management?
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the maestro orchestrating this intricate process.
It's all about ensuring the supply chain runs as smoothly, efficiently, and cost-effectively as possible.
SCM oversees each step, from the initial planning to the final delivery, coordinating between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to ensure everything clicks into place at the right time and cost.
Supply Chain Management Process
The intricacies of Supply Chain Management (SCM) are the lifelines of any business’s service or product delivery.
It's a multifaceted process that ensures the right product reaches the right consumer at the right time.
Let’s go through the core processes of SCM to unravel its complexities and explain how each stage contributes to the smooth operation of the entire supply chain.
Planning and Demand Management
Before any product can be sourced or produced, a significant amount of planning is required. This is where demand management comes into play.
Demand management is a balancing act. It requires collaboration with various departments including sales, marketing, and finance to synchronize the supply chain with the market's needs.
The results inform how a business plans its inventory, procurement, and production activities.
Procurement
Procurement is the strategic acquisition of the necessary goods and services that fuel the supply chain.
This phase involves sourcing suppliers, negotiating contracts, and purchasing raw materials or components that are crucial for the production of the final product.
It's not just about finding the lowest price; it’s about acquiring high-quality inputs that meet the business's standards without interrupting the flow of the supply chain.
Proficient procurement operations ensure that companies have what they need, when they need it, and at an acceptable cost.
Supplier relationship management becomes key, ensuring a dependable supply of materials while maintaining cost efficiency.
Production Planning
Production planning is the backbone of manufacturing operations within the supply chain.
This stage has to align closely with demand forecasting to plan for the right production volume.
Production planners must consider several elements, including capacity planning, facility management, and the coordination of resources to streamline operations.
The goal is to optimize the manufacturing process for speed, efficiency, and quality, ultimately creating an environment where orders are produced on time and within budget.
Inventory Management
An essential pillar of SCM, inventory management governs the storage and flow of goods within a company.
Poor inventory management can lead to either excess stock, which ties up capital and can become obsolete, or stock shortages, which can lead to production stops and disappointed customers.
Effective inventory management requires a precise understanding of stock requirements based on historical data and demand forecasts.
Inventory control techniques, such as Just-In-Time (JIT), are employed to reduce holding costs and maintain product quality by preventing long storage times.
Delivery and Order Fulfillment
The final phase, delivery, and order fulfillment is where the customer’s needs are ultimately met.
This process involves everything from managing orders, packing products, shipping, tracking delivery, to handling customer enquires and returns.
The efficiency of this stage is directly tied to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
This process isn’t just about delivering goods; it’s about delivering an experience.
Therefore, businesses must ensure that their order fulfillment processes are reliable, accurate, and efficient.
The Future of Supply Chain Management
The supply chain world is buzzing with innovations. As businesses and technologies evolve, SCM will become even more vital, complex, and exciting.
Let’s delves into key trends and advancements that are shaping the future of supply chain management!
Integration of Advanced Technologies
One of the most transformative factors in the future of SCM is the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT).
These technologies are set to revolutionize logistics and operation models by enhancing prediction accuracy, automating manual processes, and improving overall efficiency.
With AI and ML, supply chains can anticipate potential disruptions and automatically adjust to maintain steady operations.
IoT devices, on the other hand, enable real-time tracking of products, ensuring transparency and accountability at every stage of the supply chain.
Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Sustainability will play a pivotal role in the future of SCM as businesses become increasingly accountable for their environmental impact.
The adoption of greener supply chain practices such as sustainable sourcing, eco-friendly packaging, and reduction of carbon footprint will not only contribute to the planet's wellbeing but also appeal to the growing demographic of environmentally conscious consumers.
Ethical practices in supply chain management, including fair labor practices and equitable treatment across the supply chain, will become a standard expectation, influencing consumer loyalty and brand reputation.
Enhanced Customer-Centric Approaches
Customer expectations are continuously evolving, necessitating supply chains to become more customer-centric.
In the future, SCM will need to offer more personalized experiences, flexible delivery options, and responsive customer service.
The focus will shift toward creating seamless and engaging customer interactions from purchase to delivery, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Global Supply Chain Resiliency

The global nature of supply chains makes them susceptible to various disruptions such as geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and pandemics.
Building resilient supply chains will be a priority, with businesses strengthening their risk management strategies and diversifying their supplier base to mitigate vulnerabilities.
The future of SCM will see more emphasis on flexibility, adaptability, and building robust networks that can withstand global challenges.
Collaborative Ecosystems
Supply chains of the future will increasingly rely on collaboration and partnerships to drive innovation and efficiency.
By establishing more integrated and cooperative relationships with suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, businesses can create streamlined operations that benefit all parties involved.
Collaborative ecosystems will enable faster problem-solving, shared resources, and collective efforts toward sustainability and innovation.
Conclusion
Wrapping up, understanding and managing the supply chain can catapult a business from good to great.
As you step into this vibrant field, remember it's not just about moving products but creating a symphony of strategies, partnerships, and technologies.
In addition, as we look ahead, it is clear that the future of SCM is both challenging and filled with opportunities for growth and transformation.
Businesses that adapt, innovate, and stay ahead of these trends will chart the course for success in the evolving landscape of supply chain management.
Welcome to the future, welcome to the core of global commerce!