Overview
Understanding Modules, Objects, and Records is crucial for maximizing the functionality of Sanka.
These elements form the foundation of how data is organized, processed, and accessed in the platform.
What Are Modules in Sanka?
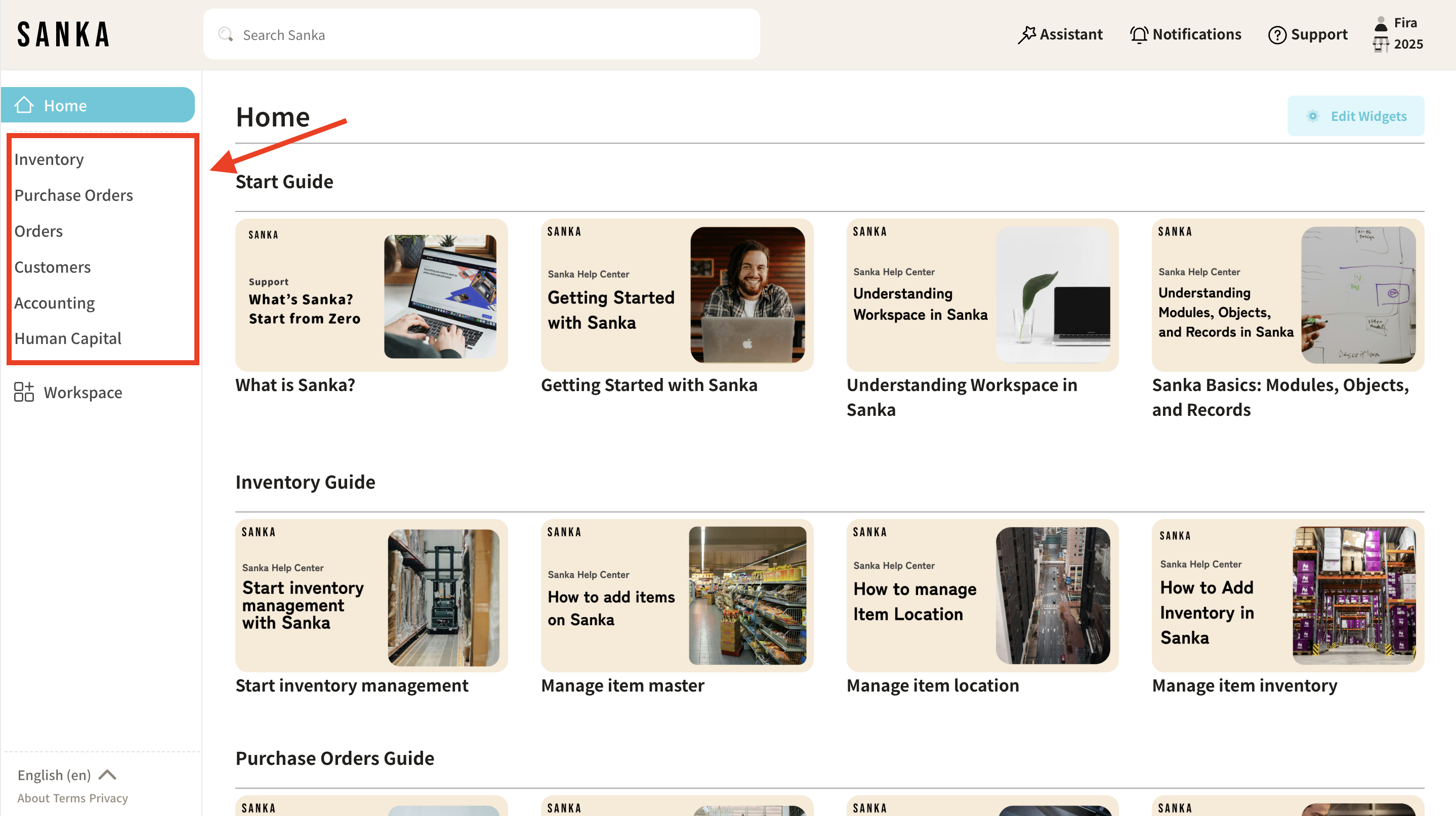
Modules in Sanka are specialized features or solutions tailored to address specific operational needs.
Each module provides tools and workflows to manage a distinct aspect of your business, such as inventory, orders, or customers.
Sanka offers the following modules:
- Inventory Management: Tracks stock levels, item details, and inventory transactions.
- Purchase Orders Management: Manages purchase orders, supplier details, and procurement workflows.
- Orders Management: Oversees customer orders, fulfillment, and delivery processes.
- Customers Management: Maintains customer profiles, interactions, and transactional data.
- Accounting Management: Handles financial records, invoicing, and expense tracking.
- Human Capital Management: Manages employee information, attendance, and HR processes.
What Are Objects?
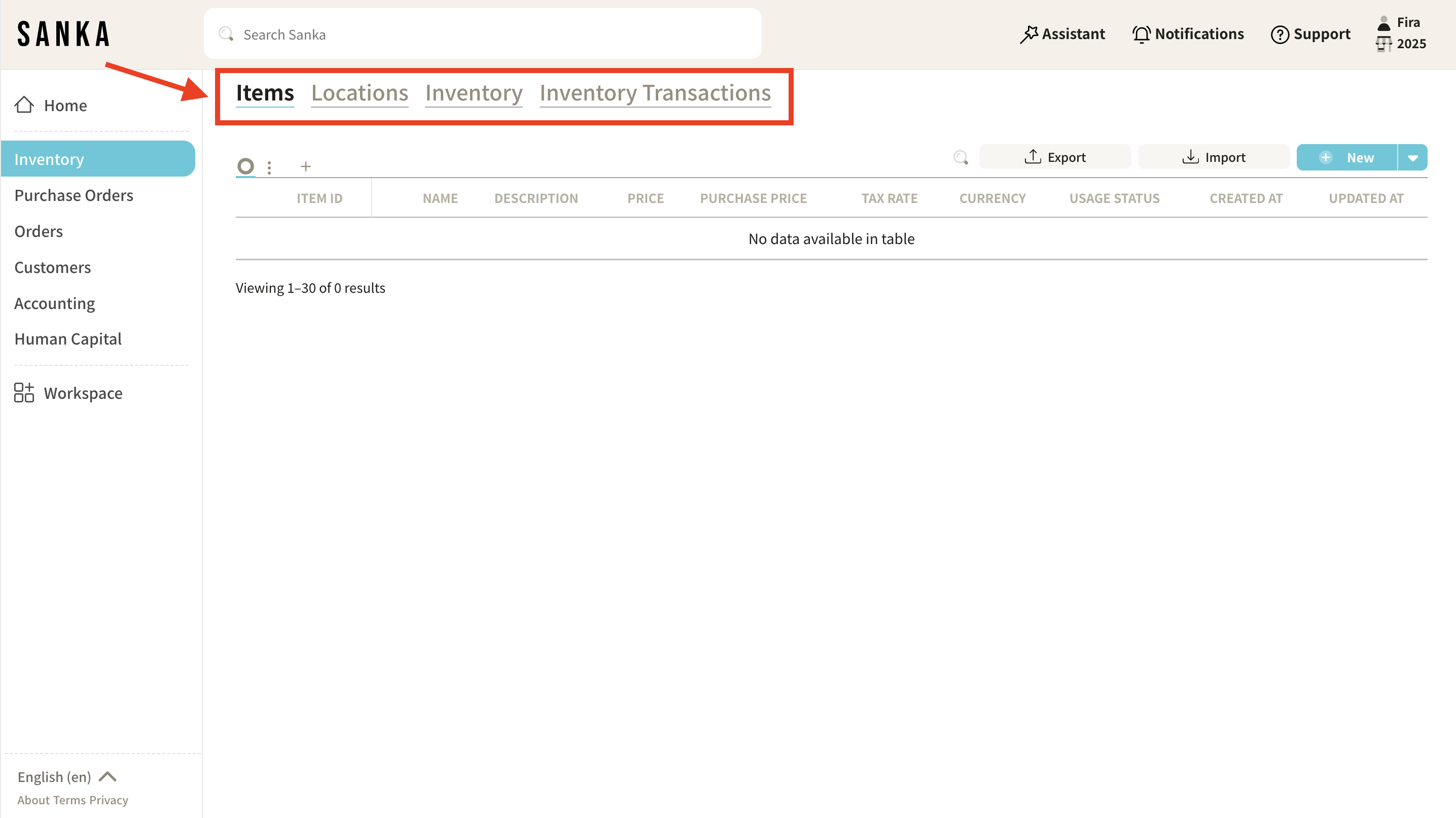
Each module contains Objects, which represent the primary data categories for that module. Objects are essentially templates that define the structure of your data.
For example:
- In Inventory Management, the default objects include: Items, Locations, Inventory, and Inventory Transactions.
- In Purchase Orders Management, the default objects include: Companies, Purchase Orders, Bills, and Workflows.
- In Orders Management, the default objects objects include: Items, Estimates, Orders, Companies, Delivery Notes, Invoices, Receipts, and Workflows.
- In Customers Management, the default objects include: Contacts, Companies, Cases, and Messages.
- In Accounting Management, the default objects include: Accounting Transactions, Orders, Slips, Expenses, Purchase Orders, and Bills.
- In Human Capital Management, the default objects include: Employees, Attendances, Reviews, Leaves, and Jobs.
These objects ensure that your data is organized and accessible for reporting, tracking, and decision-making.
What Are Records?
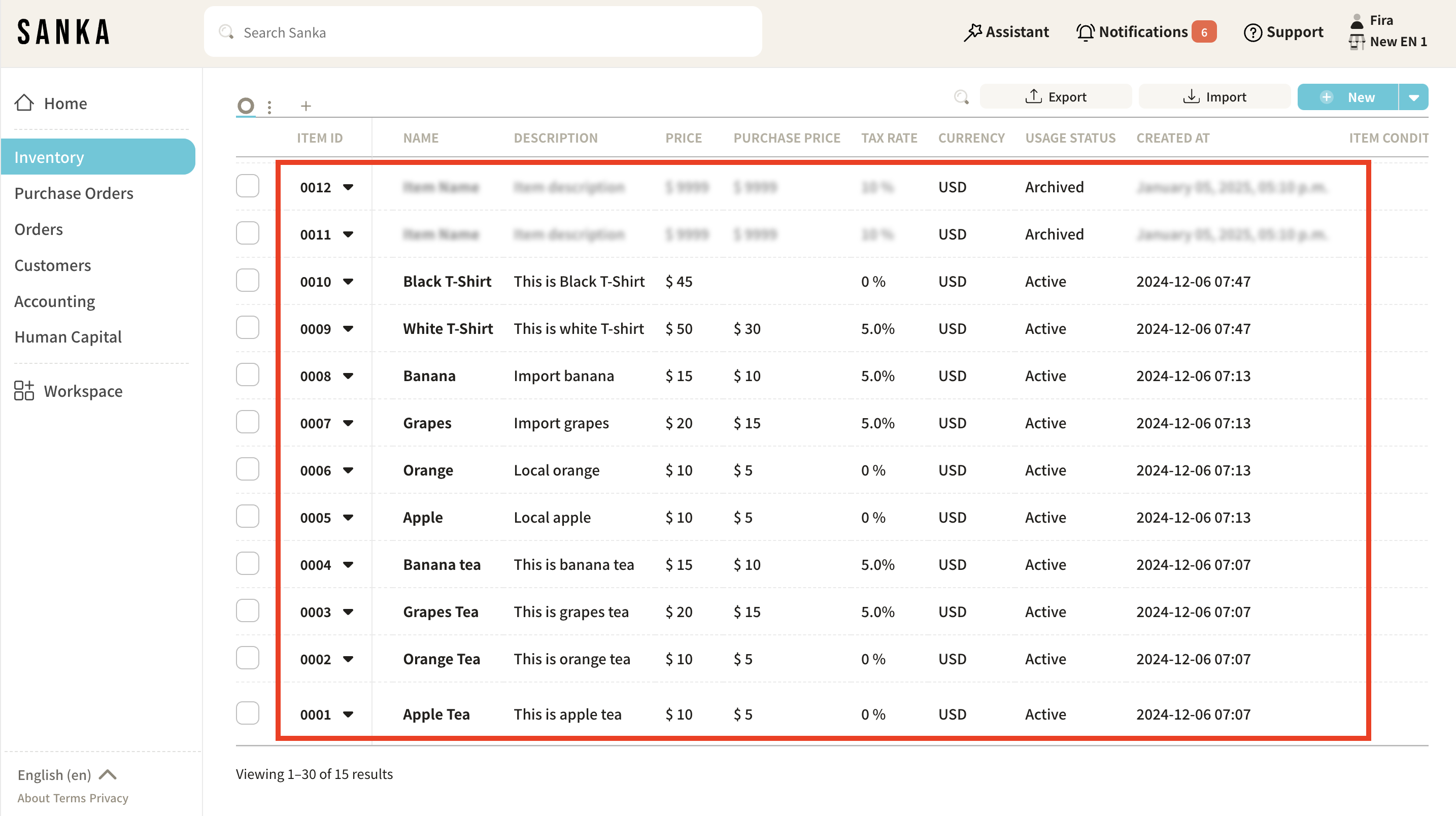
A Record is an instance of data entered into an object. For example:
- In the Orders object, a record would represent a specific customer order.
- In the Inventory Items object, a record would represent a specific product or material.
Each record is stored within its respective object and can be updated, linked to other objects, or used in reports.
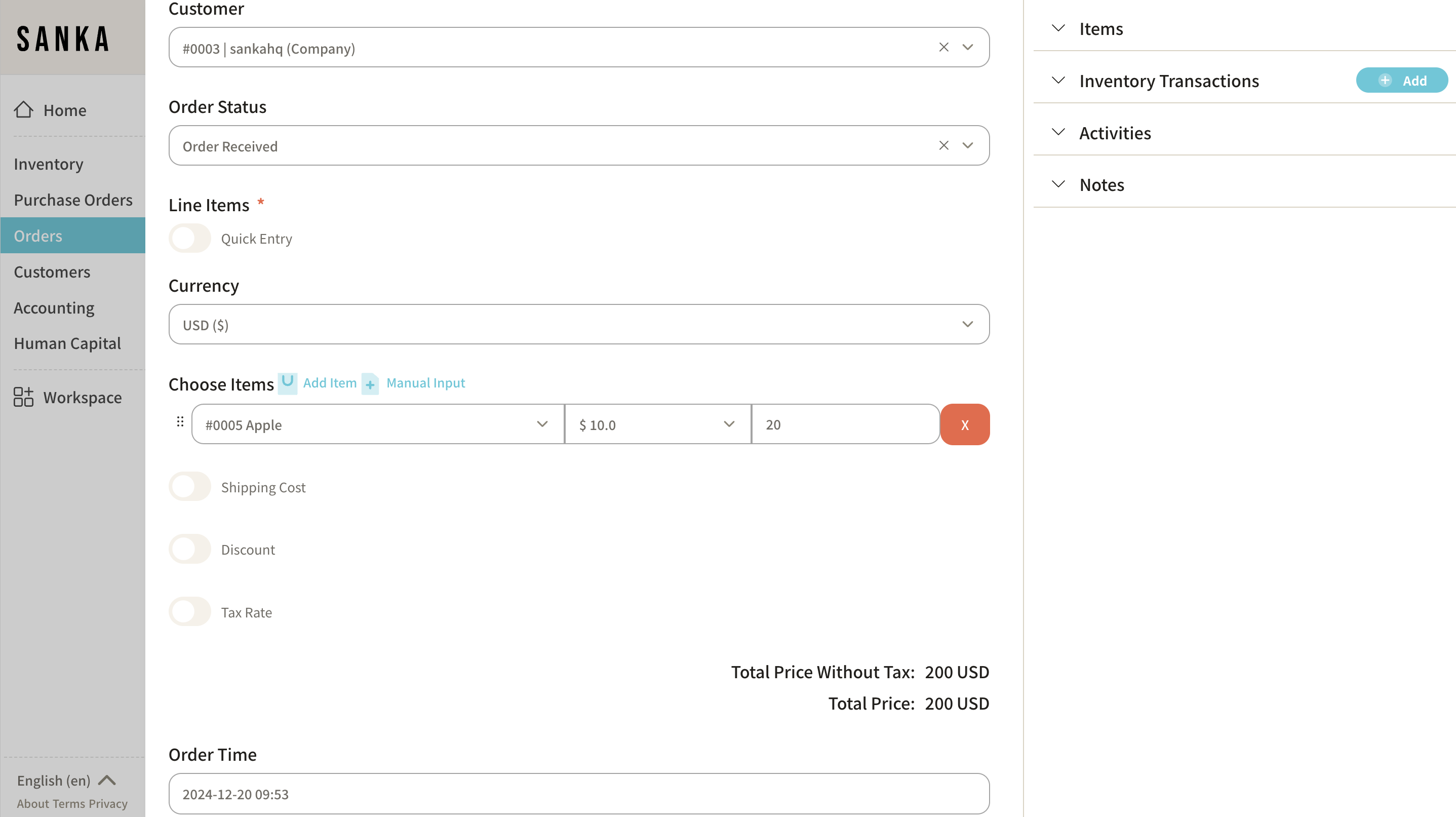
How Modules, Objects, and Records Work Together
- Modules: The overarching feature or solution (e.g., Inventory Management).
- Objects: Categories of data within the module (e.g., Items, Inventory Transactions).
- Records: Individual entries of data in an object (e.g., "Apple" in the Items object).
For example, in the Orders Management module:
- The Orders object tracks all orders.
- Each Order record contains details like customer name, order date, and total amount.
- The Order Items object tracks products in each order, with records showing item details, quantities, and prices.
Next Steps
By understanding how Modules, Objects, and Records interact, you’ll be better equipped to manage your operations efficiently and leverage Sanka’s capabilities to their fullest potential.







