Table of Contents:
- What Is Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)?
- The Benefits of Using PLM Software
- Key Elements of Product Lifecycle Management
- PLM Solutions for Different Industries
- Implementing a PLM System: Steps and Considerations
Introduction
Have you ever wondered how companies manage to conceive, design, manufacture, and retire products so efficiently?
The answer is product lifecycle management or PLM. PLM is a process that manages the entire lifecycle of a product from idea to end-of-life.
As a product manager or part of a product team, PLM can be a game changer for you. With PLM, you'll be able to oversee your product at every stage, make informed decisions, and avoid costly mistakes.
In this article, we'll explore what exactly PLM is, the major benefits it offers, and how you can implement it to boost your product's success.
By the end, you'll have a solid understanding of why PLM is critical for any company that develops physical products. Buckle up because we've got a lot to cover!
What Is Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)?
Product Lifecycle Management or PLM refers to the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its conception, through design and manufacture, to service and disposal.
Using PLM software, companies can track key details about a product, like specifications, parts, and requirements. This helps teams collaborate more easily and speeds up development.
It's a strategy that orchestrates collaboration, data management, and business processes, striving to make every product's journey as seamless as possible.
PLM's reach extends across the four principal stages of the product lifecycle:
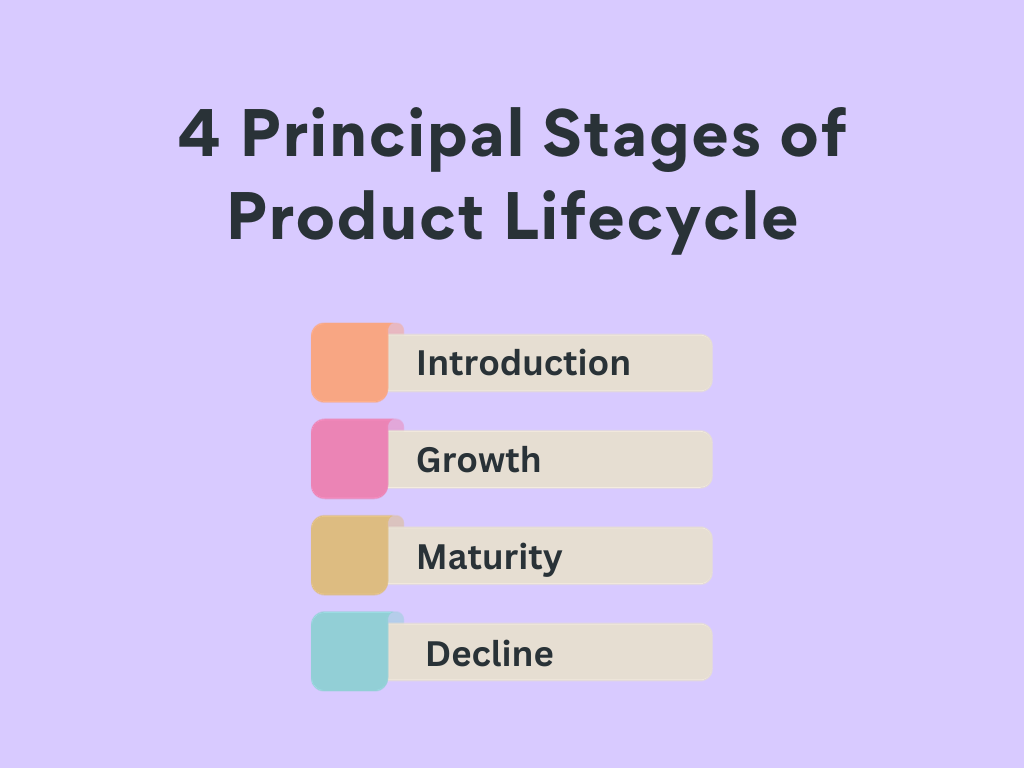
- Introduction which encompasses the conceptualization and design of the product.
- Growth where the product starts to gain traction in the marketplace.
- Maturity, the stage at which product sales peak, and
- Decline where market saturation leads to a gradual drop-off in sales.
The Benefits of Using PLM Software
Using PLM software has a lot of benefits for your business.
Cost and Time Savings
PLM helps reduce costs in many ways. It streamlines product design and development, decreasing the time it takes to get a product to market.
This efficiency results in lower labor and material costs. PLM also reduces redundant data entry and minimizes errors, saving time and money.
Improved Collaboration
With PLM, your whole product team can work together in one place. All departments, like design, engineering, and manufacturing, can view and share live data in real-time.
This makes collaboration much easier and helps avoid miscommunications. Tasks, changes, and approvals can be managed within the software, keeping everyone on the same page.
Enhanced Product Quality
PLM gives you more control and visibility over product data, which leads to higher-quality products. It ensures best practices and standards are followed in the design process.
PLM also provides a single source of truth for product information, so there is no confusion about the current design or revision.
Compliance requirements can be built in to automatically check products meet certain standards.
Better Decision Making
PLM provides insights that help guide business decisions. Real-time access to product data, costs, and key performance indicators allows you to spot issues early and make data-driven choices.
You can see how changes to a product will impact schedules, resources, and budgets before implementing them. PLM supports a proactive approach so you can avoid risks, reduce waste, and optimize results.
Key Elements of Product Lifecycle Management
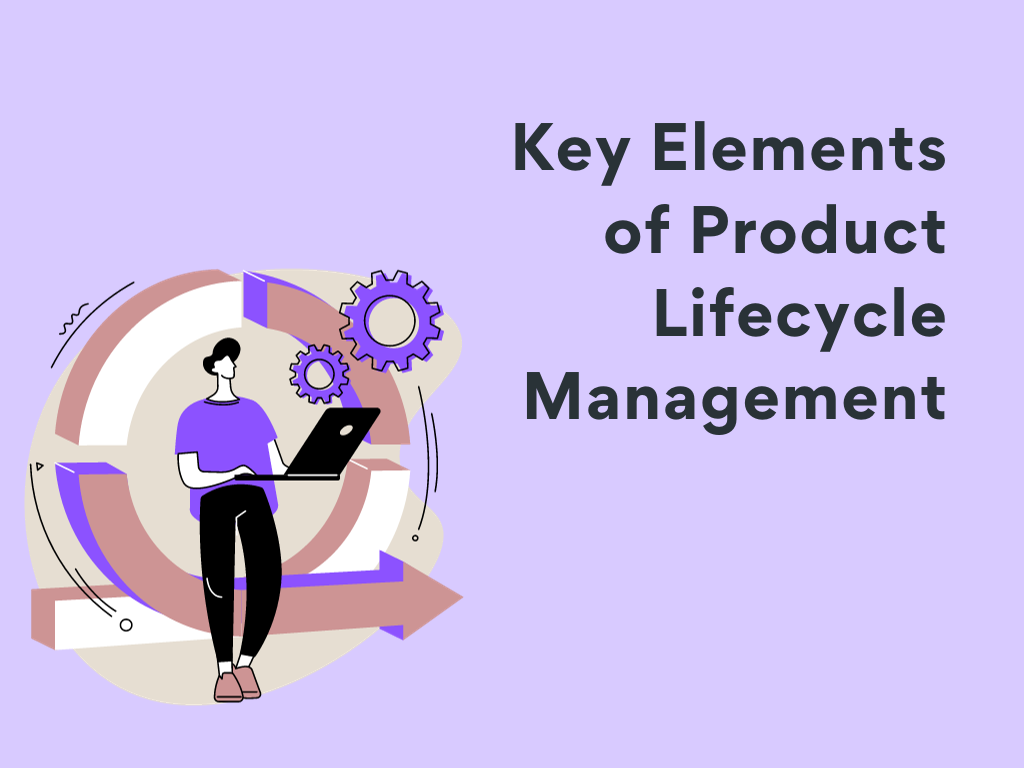
PLM can be orchestrated via its four integral elements: people, process, data, and technology.
People
The people involved in a product's lifecycle are the linchpin of PLM.
This aspect includes everyone from the designers and engineers crafting the product to the marketing team bringing it to the marketplace, to the after-sales service crew.
Collaborative communication among these players leads to efficient PLM.
Process
The processes form the framework of a product's lifecycle. These predefined operational steps guide a product from the drawing board right through to the consumer's hands.
The process element of PLM ensures standardization, repeatability, and reliability, paving the way for reduced time to market and improved product quality.
Data
The data component of PLM encapsulates all the product-related information captured and utilized during its lifecycle.
This includes design data, market research, manufacturing data, post-sale performance stats, and even disposal information.
Consolidating this data helps in effective decision-making, risk mitigation, and continuous improvement.
Technology
Last but not least, technology is the catalyzing force that binds all the other elements of PLM together.
PLM software allows the effective capture, management, dissemination, and utilization of data and facilitates process management while enhancing collaboration among the involved parties.
PLM Solutions for Different Industries

PLM software is tailored to the specific needs of different industries. Some of the major solutions include:
Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies were early adopters of PLM and used it to manage the design, production, and distribution of physical products.
PLM helps streamline the process from idea generation to a finished product on the shelf.
It provides a single source of truth for all product data that everyone from designers to suppliers to retailers can access.
Retail
Retailers have complex product portfolios and short product lifecycles. PLM helps them get new products to market quickly while managing costs.
It gives visibility into which products are performing well so retailers can make data-driven decisions about what to promote or discontinue.
PLM also helps retailers ensure their private label products meet all compliance and regulatory requirements before hitting the sales floor.
Consumer Packaged Goods
Like retail, the consumer packaged goods (CPG) industry moves at a fast pace. In addition to managing short product lifecycles, CPG companies have to handle many product variations, sizes, and packaging options.
PLM provides a centralized system to organize all product data in one place. It streamlines processes such as formula and package design, compliance management, and quality control.
CPG companies use PLM to get high-quality, compliant products into the hands of customers as quickly as possible.
Life Sciences
For pharmaceutical, medical device, and biotech companies, properly managing product data is a matter of life and death.
PLM offers a secure, validated system for organizing and controlling sensitive product information. It helps facilitate processes such as clinical trial management, regulatory submissions, quality control, and product maintenance.
Life science companies rely on PLM to bring life-changing products to market while ensuring safety, efficacy, and compliance every step of the way.
Implementing a PLM System: Steps and Considerations
Once you’ve decided to adopt a PLM system, it’s time to implement it. This is no small task and requires careful planning to do right. Here are some steps and considerations to keep in mind:
Determine your requirements
First, figure out exactly what you need the PLM software to do. Do you want it primarily for design and engineering? Or also for sourcing, manufacturing, and service management?
Define all the capabilities required to support your product processes. Talk to stakeholders in each department to understand their needs.
Select a solution
With requirements in hand, you can evaluate solutions that meet your needs. Consider both broad, enterprise-level platforms and more specialized, niche products.
Compare offerings from vendors like PTC, Oracle, SAP, Dassault, and Siemens. Choose a cloud-based or on-premise system. Think about cost, scalability, integration, and user experience.
Prepare your data
Before implementing the new PLM system, review and organize your existing product data. Determine what should be migrated to the PLM software.
Clean up file names, properties, classifications, and any incorrect or outdated information. Having your data in order will make the migration and transition smoother.
Plan the rollout
Create a detailed schedule for deploying the PLM solution. Determine who will be involved, the required training, data migration, testing, and go-live dates for each product line or department.
Start with a pilot group to work out any issues before widespread adoption. Get stakeholders on board and address any concerns early on.
Train and support users
Conduct training for all users on the functionality and interface of the new PLM system. Offer both initial and ongoing support to help them get up to speed.
Monitor how people are using the software and make any needed customizations or changes to improve the user experience. Stay up-to-date with upgrades and new features offered by the vendor.
Review and optimize
Once the PLM software has been in use for a few months, evaluate how it’s working. Get feedback from all users on what’s going well and any pain points.
Make tweaks or adjustments to business processes or system configuration as needed. PLM implementation is an ongoing process of continuous improvement.
With time and experience, you’ll maximize the value of your product lifecycle management solution.
Conclusion
So there you have it, a deep dive into PLM and how it can revolutionize your business. By now you should have a solid understanding of what PLM is, why companies implement it, and how you can leverage it to gain a competitive advantage.
The benefits of improved productivity, cost savings, and faster time to market are huge. What are you waiting for? Talk to your team and start evaluating PLM solutions.
Find one tailored to your unique needs and business model. Then sit back and watch as PLM transforms how you develop, manufacture, and deliver products to customers. The future is digital, and PLM is how you get there.